资源嵌入
PostgREST 允许在单个 API 调用中包含相关资源。这减少了对多个 API 请求的需求。
外键连接
服务器使用 **外键** 来确定哪些数据库对象可以连接在一起。它支持连接表、视图和表值函数。
对于表,它使用外键列(尊重复合键)生成连接条件。
对于视图,它使用视图的基表外键列生成连接条件。
对于表值函数,它根据返回的表类型的外键列生成连接条件。
重要
每当外键发生更改时,您必须执行 模式缓存重新加载 才能使此功能正常工作。
关系
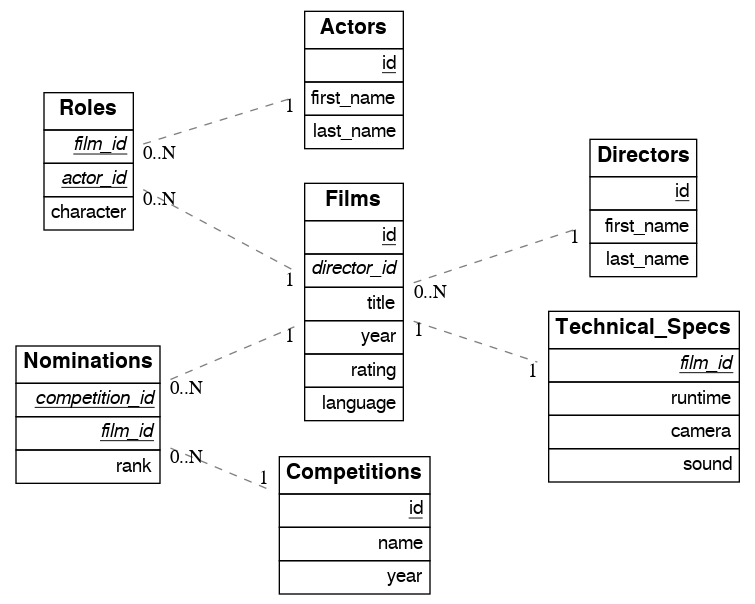
例如,考虑一个电影及其奖项的数据库
create table actors(
id int primary key generated always as identity,
first_name text,
last_name text
);
create table directors(
id int primary key generated always as identity,
first_name text,
last_name text
);
create table films(
id int primary key generated always as identity,
director_id int references directors(id),
title text,
year int,
rating numeric(3,1),
language text
);
create table technical_specs(
film_id int references films(id) primary key,
runtime time,
camera text,
sound text
);
create table roles(
film_id int references films(id),
actor_id int references actors(id),
character text,
primary key(film_id, actor_id)
);
create table competitions(
id int primary key generated always as identity,
name text,
year int
);
create table nominations(
competition_id int references competitions(id),
film_id int references films(id),
rank int,
primary key (competition_id, film_id)
);
多对一关系
由于 films 对 directors 有一个 **外键**,这建立了一个多对一关系。这使我们能够请求所有电影以及每部电影的导演。
curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,directors(id,last_name)"
[
{ "title": "Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory In Lyon",
"directors": {
"id": 2,
"last_name": "Lumière"
}
},
{ "title": "The Dickson Experimental Sound Film",
"directors": {
"id": 1,
"last_name": "Dickson"
}
},
{ "title": "The Haunted Castle",
"directors": {
"id": 3,
"last_name": "Méliès"
}
}
]
请注意,嵌入的 directors 由于“一对一”端而作为 JSON 对象返回。
由于表名是复数,我们可以通过使用别名将其变为单数来更准确。
curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,director:directors(id,last_name)"
[
{ "title": "Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory In Lyon",
"director": {
"id": 2,
"last_name": "Lumière"
}
},
".."
]
一对多关系
**外键引用** 建立了反向一对多关系。在这种情况下,films 由于“多对一”端而作为 JSON 数组返回。
curl "https://:3000/directors?select=last_name,films(title)"
[
{ "last_name": "Lumière",
"films": [
{"title": "Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory In Lyon"}
]
},
{ "last_name": "Dickson",
"films": [
{"title": "The Dickson Experimental Sound Film"}
]
},
{ "last_name": "Méliès",
"films": [
{"title": "The Haunted Castle"}
]
}
]
多对多关系
联接表确定多对多关系。它必须包含指向其他两个表的外部键,并且它们必须是其复合键的一部分。在 示例电影数据库 中,roles 被视为联接表。
如果复合键包含其他列,也会检测到连接表。
create table roles(
id int generated always as identity,
, film_id int references films(id)
, actor_id int references actors(id)
, character text,
, primary key(id, film_id, actor_id)
);
curl "https://:3000/actors?select=first_name,last_name,films(title)"
[
{ "first_name": "Willem",
"last_name": "Dafoe",
"films": [
{"title": "The Lighthouse"}
]
},
".."
]
一对一关系
一对一关系可以通过两种方式检测到。
当外键是主键时,如 示例电影数据库 中所指定。
当外键具有唯一约束时。
create table technical_specs( film_id int references films(id) unique, runtime time, camera text, sound text );
curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,technical_specs(camera)"
[
{
"title": "Pulp Fiction",
"technical_specs": {"camera": "Arriflex 35-III"}
},
".."
]
计算关系
您可以使用函数手动定义关系。这对于无法定义外键的数据库对象很有用,例如 外部数据包装器。
假设有一个外部表 premieres,我们希望将其与 films 关联。
create foreign table premieres (
id integer,
location text,
"date" date,
film_id integer
) server import_csv options ( filename '/tmp/directors.csv', format 'csv');
create function film(premieres) returns setof films rows 1 as $$
select * from films where id = $1.film_id
$$ stable language sql;
上面的函数定义了 premieres(参数)和 films(返回类型)之间的关系。由于存在 rows 1,因此定义了多对一关系。函数名称 film 是任意的,可以用于进行嵌入。
curl "https://:3000/premieres?select=location,film(name)"
[
{
"location": "Cannes Film Festival",
"film": {"name": "Pulp Fiction"}
},
".."
]
现在让我们定义相反的一对多关系。
create function premieres(films) returns setof premieres as $$
select * from premieres where film_id = $1.id
$$ stable language sql;
在这种情况下,PostgreSQL 定义了一个隐式的 ROWS 1000(在此 PostgreSQL 文档中搜索“result_rows”)。我们认为任何大于 1 的值都是“多”,因此这定义了一对多关系。
curl "https://:3000/films?select=name,premieres(name)"
[
{
"name": "Pulp Ficiton",
"premieres": [{"location": "Cannes Festival"}]
},
".."
]
覆盖关系
计算关系还允许您覆盖 PostgREST 自动检测的关系。
例如,要覆盖 films 和 directors 之间的 多对一关系。
create function directors(films) returns setof directors rows 1 as $$
select * from directors where id = $1.director_id
$$ stable language sql;
由于函数重载,您可以对不同的参数使用相同的函数名。因此,从其他表/视图定义到导演的关系。
create function directors(film_schools) returns setof directors as $$
select * from directors where film_school_id = $1.id
$$ stable language sql;
计算关系具有良好的性能,因为它们的设计意图允许 函数内联。
警告
在创建计算关系时始终使用
SETOF。函数可以在不使用SETOF的情况下返回一个表,但请记住,PostgreSQL 不会内联它们。确保正确标记关系的
to-one部分。当使用ROWS 1估计时,PostgREST 会期望返回单行。如果不是这种情况,它将展开嵌入并为顶级资源返回重复的值。
多个外键关系上的外键连接
当表之间存在多个外键时,外键连接 需要消除歧义以确定要用于连接的外键列。为此,您可以使用 !<fk> 语法指定外键。
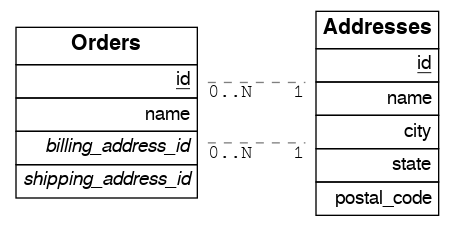
多个多对一
例如,假设您有以下 orders 和 addresses 表
create table addresses (
id int primary key generated always as identity,
name text,
city text,
state text,
postal_code char(5)
);
create table orders (
id int primary key generated always as identity,
name text,
billing_address_id int,
shipping_address_id int,
constraint billing foreign key(billing_address_id) references addresses(id),
constraint shipping foreign key(shipping_address_id) references addresses(id)
);
由于 orders 表有两个指向 addresses 表的外键,因此外键连接存在歧义,PostgREST 将返回错误
curl "https://:3000/orders?select=*,addresses(*)" -i
HTTP/1.1 300 Multiple Choices
{
"code": "PGRST201",
"details": [
{
"cardinality": "many-to-one",
"embedding": "orders with addresses",
"relationship": "billing using orders(billing_address_id) and addresses(id)"
},
{
"cardinality": "many-to-one",
"embedding": "orders with addresses",
"relationship": "shipping using orders(shipping_address_id) and addresses(id)"
}
],
"hint": "Try changing 'addresses' to one of the following: 'addresses!billing', 'addresses!shipping'. Find the desired relationship in the 'details' key.",
"message": "Could not embed because more than one relationship was found for 'orders' and 'addresses'"
}
要成功将 orders 与 addresses 连接,我们可以遵循错误 hint,它告诉我们将外键名称添加为 !billing 或 !shipping。请注意,外键已在 上面的 SQL 定义 中显式命名。为了使结果更清晰,我们还将对表进行别名
# curl "https://:3000/orders?select=name,billing_address:addresses!billing(name),shipping_address:addresses!shipping(name)"
curl --get "https://:3000/orders" \
-d "select=name,billing_address:addresses!billing(name),shipping_address:addresses!shipping(name)"
[
{
"name": "Personal Water Filter",
"billing_address": {
"name": "32 Glenlake Dr.Dearborn, MI 48124"
},
"shipping_address": {
"name": "30 Glenlake Dr.Dearborn, MI 48124"
}
}
]
多个一对多
让我们从 多个多对一 中获取表。要获得相反的一对多关系,我们也可以指定外键名称
# curl "https://:3000/addresses?select=name,billing_orders:orders!billing(name),shipping_orders!shipping(name)&id=eq.1"
curl --get "https://:3000/addresses" \
-d "select=name,billing_orders:orders!billing(name),shipping_orders!shipping(name)" \
-d "id=eq.1"
[
{
"name": "32 Glenlake Dr.Dearborn, MI 48124",
"billing_orders": [
{ "name": "Personal Water Filter" },
{ "name": "Coffee Machine" }
],
"shipping_orders": [
{ "name": "Coffee Machine" }
]
}
]
递归关系
为了消除递归关系的歧义,PostgREST 需要使用 计算关系。
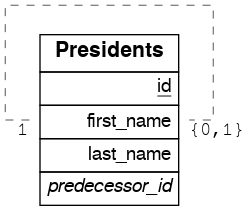
递归一对一
create table presidents (
id int primary key generated always as identity,
first_name text,
last_name text,
predecessor_id int references presidents(id) unique
);
要获取递归一对一关系的任一端,请创建以下函数
create or replace function predecessor(presidents) returns setof presidents rows 1 as $$
select * from presidents where id = $1.predecessor_id
$$ stable language sql;
create or replace function successor(presidents) returns setof presidents rows 1 as $$
select * from presidents where predecessor_id = $1.id
$$ stable language sql;
现在,要查询总统及其前任和继任者
# curl "https://:3000/presidents?select=last_name,predecessor(last_name),successor(last_name)&id=eq.2"
curl --get "https://:3000/presidents" \
-d "select=last_name,predecessor(last_name),successor(last_name)" \
-d "id=eq.2"
[
{
"last_name": "Adams",
"predecessor": {
"last_name": "Washington"
},
"successor": {
"last_name": "Jefferson"
}
}
]
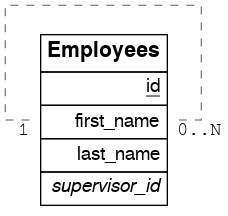
递归一对多
create table employees (
id int primary key generated always as identity,
first_name text,
last_name text,
supervisor_id int references employees(id)
);
要获取一对多嵌入,即主管及其下属,请创建类似于以下的函数
create or replace function supervisees(employees) returns setof employees as $$
select * from employees where supervisor_id = $1.id
$$ stable language sql;
现在,查询将是
# curl "https://:3000/employees?select=last_name,supervisees(last_name)&id=eq.1"
curl --get "https://:3000/employees" \
-d "select=last_name,supervisees(last_name)" \
-d "id=eq.1"
[
{
"name": "Taylor",
"supervisees": [
{ "name": "Johnson" },
{ "name": "Miller" }
]
}
]
递归多对一
让我们使用 递归一对多 中的相同 employees 表。要获取多对一关系,即员工及其各自的主管,您需要创建类似于以下的函数
create or replace function supervisor(employees) returns setof employees rows 1 as $$
select * from employees where id = $1.supervisor_id
$$ stable language sql;
然后,查询将是
# curl "https://:3000/employees?select=last_name,supervisor(last_name)&id=eq.3"
curl --get "https://:3000/employees" \
-d "select=last_name,supervisor(last_name)" \
-d "id=eq.3"
[
{
"last_name": "Miller",
"supervisor": {
"last_name": "Taylor"
}
}
]
递归多对多
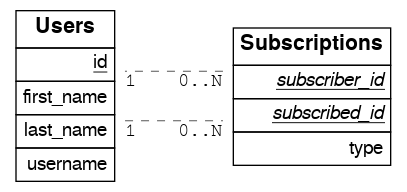
create table users (
id int primary key generated always as identity,
first_name text,
last_name text,
username text unique
);
create table subscriptions (
subscriber_id int references users(id),
subscribed_id int references users(id),
type text,
primary key (subscriber_id, subscribed_id)
);
要获取用户的全部订阅者以及他们正在关注的用户,请定义以下函数
create or replace function subscribers(users) returns setof users as $$
select u.*
from users u,
subscriptions s
where s.subscriber_id = u.id and
s.subscribed_id = $1.id
$$ stable language sql;
create or replace function following(users) returns setof users as $$
select u.*
from users u,
subscriptions s
where s.subscribed_id = u.id and
s.subscriber_id = $1.id
$$ stable language sql;
然后,请求将是
# curl "https://:3000/users?select=username,subscribers(username),following(username)&id=eq.4"
curl --get "https://:3000/users" \
-d "select=username,subscribers(username),following(username)" \
-d "id=eq.4"
[
{
"username": "the_top_artist",
"subscribers": [
{ "username": "patrick109" },
{ "username": "alicia_smith" }
],
"following": [
{ "username": "top_streamer" }
]
}
]
分区表上的外键连接
外键连接也可以在 分区表 和其他表之间进行。
例如,让我们创建 box_office 分区表,其中包含电影的每日总收入
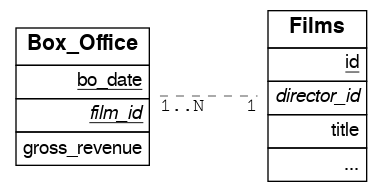
CREATE TABLE box_office (
bo_date DATE NOT NULL,
film_id INT REFERENCES films NOT NULL,
gross_revenue DECIMAL(12,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (bo_date, film_id)
) PARTITION BY RANGE (bo_date);
-- Let's also create partitions for each month of 2021
CREATE TABLE box_office_2021_01 PARTITION OF box_office
FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-01-01') TO ('2021-01-31');
CREATE TABLE box_office_2021_02 PARTITION OF box_office
FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-02-01') TO ('2021-02-28');
-- and so until december 2021
由于它包含 films_id 外键,因此可以连接 box_office 和 films
# curl "https://:3000/box_office?select=bo_date,gross_revenue,films(title)&gross_revenue=gte.1000000"
curl --get "https://:3000/box_office" \
-d "select=bo_date,gross_revenue,films(title)" \
-d "gross_revenue=gte.1000000"
注意
不允许对分区进行外键连接,因为这会导致它们与其父分区表之间的歧义错误(请参阅 多个外键关系上的外键连接)。如果需要,可以使用 计算关系。
分区表可以从 PostgreSQL 11 开始引用其他表,但只能从 PostgreSQL 12 开始被其他任何表引用。
视图上的外键连接
PostgREST 将使用视图的基础表推断视图的外键。基础表是在视图定义的 FROM 和 JOIN 子句中引用的表。外键的列必须出现在视图的顶部 SELECT 子句中才能使此方法起作用。
例如,以下视图具有 nominations、films 和 competitions 作为基础表
CREATE VIEW nominations_view AS
SELECT
films.title as film_title
, competitions.name as competition_name
, nominations.rank
, nominations.film_id as nominations_film_id
, films.id as film_id
FROM nominations
JOIN films ON films.id = nominations.film_id
JOIN competitions ON competitions.id = nominations.competition_id;
由于此视图包含 nominations.film_id,它与 films 表具有 **外键** 关系,因此我们可以连接 films 表。类似地,因为视图包含 films.id,所以我们也可以连接 roles 和 actors 表(最后一个是多对多关系)。
# curl "https://:3000/nominations_view?select=film_title,films(language),roles(character),actors(last_name,first_name)&rank=eq.5"
curl --get "https://:3000/nominations_view" \
-d "select=film_title,films(language),roles(character),actors(last_name,first_name)" \
-d "rank=eq.5"
也可以对 物化视图 进行外键连接。
重要
不能保证外键连接对所有类型的视图都有效。特别是,外键连接不适用于包含 UNION 的视图。
为什么?PostgREST 通过查询和解析 pg_rewrite 来检测视图中的基表外键。这可能会根据视图的复杂性而失败。
作为解决方法,您可以使用 计算关系 为视图定义手动关系。
如果视图定义发生更改,您必须刷新 PostgREST 的模式缓存才能使其正常工作。请参阅 模式缓存重新加载 部分。
视图链上的外键连接
视图也可以依赖于其他视图,而这些视图又依赖于实际的基表。为了让 PostgREST 递归地拾取这些链到任何深度,所有视图都必须在搜索路径中,因此要么在公开的模式 (db-schemas) 中,要么在 db-extra-search-path 中设置的某个模式中。这并不适用于基表,基表也可以在私有模式中。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 模式隔离。
表值函数上的外键连接
如果您有一个 函数 返回表类型,您可以在结果上进行外键连接。
这是一个示例函数(注意 RETURNS SETOF films)。
CREATE FUNCTION getallfilms() RETURNS SETOF films AS $$
SELECT * FROM films;
$$ LANGUAGE SQL STABLE;
包含 directors 的请求
# curl "https://:3000/rpc/getallfilms?select=title,directors(id,last_name)&title=like.*Workers*"
curl --get "https://:3000/rpc/getallfilms" \
-d "select=title,directors(id,last_name)" \
-d "title=like.*Workers*"
[
{ "title": "Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory In Lyon",
"directors": {
"id": 2,
"last_name": "Lumière"
}
}
]
写入上的外键连接
在执行 插入、更新 或 删除 操作后,您可以将相关的数据库对象连接起来。
例如,您想插入一部电影,然后获取其部分属性并连接其导演。
curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,year,director:directors(first_name,last_name)" \
-H "Prefer: return=representation" \
-d @- << EOF
{
"id": 100,
"director_id": 40,
"title": "127 hours",
"year": 2010,
"rating": 7.6,
"language": "english"
}
EOF
响应
{
"title": "127 hours",
"year": 2010,
"director": {
"first_name": "Danny",
"last_name": "Boyle"
}
}
嵌套嵌入
如果您想通过连接表进行嵌入,但需要对中间资源有更多控制,您可以进行嵌套嵌入。例如,您可以请求演员、他们的角色以及这些角色的电影。
curl "https://:3000/actors?select=roles(character,films(title,year))"
嵌入式过滤器
嵌入式资源的塑造方式类似于其顶层资源。为此,请在查询参数前加上嵌入式资源的名称。例如,要对每部电影中的演员进行排序
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=*,actors(*)&actors.order=last_name,first_name"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=*,actors(*)" \
-d "actors.order=last_name,first_name"
这会对每部电影中的演员列表进行排序,但不会改变电影本身的顺序。要过滤每部电影返回的角色
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=*,roles(*)&roles.character=in.(Chico,Harpo,Groucho)"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=*,roles(*)" \
-d "roles.character=in.(Chico,Harpo,Groucho)"
同样,这会将包含的角色限制在某些角色,但不会以任何方式过滤电影。没有这些角色的电影将与空角色列表一起包含。
可以使用 or 过滤器进行类似的操作
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=*,roles(*)&roles.or=(character.eq.Gummo,character.eq.Zeppo)"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=*,roles(*)" \
-d "roles.or=(character.eq.Gummo,character.eq.Zeppo)"
但是,这仅适用于 roles 内的列。请参阅 如何在多个资源中使用“或”。
限制和偏移操作是可能的
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=*,actors(*)&actors.limit=10&actors.offset=2"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=*,actors(*)" \
-d "actors.limit=10" \
-d "actors.offset=2"
嵌入式资源可以被别名化,并且可以对这些别名应用过滤器
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=*,actors(*)&actors.limit=10&actors.offset=2"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=*,90_comps:competitions(name),91_comps:competitions(name)" \
-d "90_comps.year=eq.1990" \
-d "91_comps.year=eq.1991"
过滤器也可以应用于嵌套的嵌入式资源
curl "https://:3000/films?select=*,roles(*,actors(*))&roles.actors.order=last_name&roles.actors.first_name=like.*Tom*"
结果将显示名为 Tom 的嵌套演员,并按姓氏排序。别名也可以用作资源名称来过滤嵌套表。
顶层过滤
默认情况下,嵌入式过滤器 不会更改顶层资源 (films) 行
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,actors(first_name,last_name)&actors.first_name=eq.Jehanne
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=title,actors(first_name,last_name)" \
-d "actors.first_name=eq.Jehanne"
[
{
"title": "Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory In Lyon",
"actors": []
},
{
"title": "The Dickson Experimental Sound Film",
"actors": []
},
{
"title": "The Haunted Castle",
"actors": [
{
"first_name": "Jehanne",
"last_name": "d'Alcy"
}
]
}
]
为了过滤顶层行,您需要在嵌入式资源中添加 !inner。例如,要获取仅包含名为 Jehanne 的演员的电影
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,actors!inner(first_name,last_name)&actors.first_name=eq.Jehanne"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=title,actors!inner(first_name,last_name)" \
-d "actors.first_name=eq.Jehanne"
[
{
"title": "The Haunted Castle",
"actors": [
{
"first_name": "Jehanne",
"last_name": "d'Alcy"
}
]
}
]
嵌入资源的空值过滤
嵌入资源的空值过滤可以与 !inner 的行为相同,但更灵活。
例如,执行 actors=not.is.null 返回的结果与 actors!inner(*) 相同。
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,actors(*)&actors=not.is.null"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=title,actors(*)" \
-d "actors=not.is.null"
在嵌入资源中可以使用 is.null 过滤器执行反连接。获取所有没有提名的电影。
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,nominations()&nominations=is.null"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=title,nominations()" \
-d "nominations=is.null"
is.null 和 not.is.null 都可以包含在 or 运算符中。例如,要获取没有演员或导演注册的电影。
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,nominations()&nominations=is.null"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d select=title,actors(*),directors(*)" \
-d "or=(actors.is.null,directors.is.null)"
跨嵌入资源的 OR 过滤
您也可以使用 not.is.null 在多个资源上进行 or 过滤。例如,要显示演员或导演名为 John 的电影。
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,actors(),directors()&directors.first_name=eq.John&actors.first_name=eq.John&or=(directors.not.is.null,actors.not.is.null)"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=title,actors(),directors()" \
-d "directors.first_name=eq.John" \
-d "actors.first_name=eq.John" \
-d "or=(directors.not.is.null,actors.not.is.null)"
[
{ "title": "Pulp Fiction" },
{ "title": "The Thing" },
".."
]
这里,我们使用 空嵌入,因为检索其信息将受到过滤器的限制。例如,如果 directors 嵌入的 first_name 不是 John,则它将返回 null。要解决此问题,您需要添加额外的嵌入资源,并使用空嵌入资源进行过滤。从上面的例子来看
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,act:actors(),dir:directors(),actors(first_name),directors(first_name)&dir.first_name=eq.John&act.first_name=eq.John&or=(dir.not.is.null,act.not.is.null)"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
# We need to use aliases like "act" and "dir" to filter the empty embeds
-d "select=title,act:actors(),dir:directors(),actors(first_name),directors(first_name)" \
-d "dir.first_name=eq.John" \
-d "act.first_name=eq.John" \
-d "or=(dir.not.is.null,act.not.is.null)"
[
{
"title": "Pulp Fiction",
"actors": [
{ "first_name": "John" },
{ "first_name": "Samuel" },
{ "first_name": "Uma" },
".."
]
"directors": {
"first_name": "Quentin"
}
},
".."
]
空嵌入
您可以将嵌入资源留空,这在某些情况下有助于过滤。
按演员过滤电影,但不包含它们。
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,actors()&actors.first_name=eq.Jehanne&actors=not.is.null"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=title,actors()" \
-d "actors.first_name=eq.Jehanne" \
-d "actors=not.is.null"
[
{
"title": "The Haunted Castle",
}
]
顶层排序
在 多对一 和 一对一 关系中,您可以使用“一对一”端的列对顶层进行排序。
例如,使用导演的姓氏按降序排列电影。
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,directors(last_name)&order=directors(last_name).desc"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=title,directors(last_name)" \
-d "order=directors(last_name).desc"
扩展嵌入资源
在多对一和一对一关系中,您可以“扩展”嵌入资源。也就是说,删除嵌入资源列周围的 JSON 对象。
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,...directors(director_last_name:last_name)&title=like.*Workers*"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=title,...directors(director_last_name:last_name)" \
-d "title=like.*Workers*"
[
{
"title": "Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory In Lyon",
"director_last_name": "Lumière"
}
]
请注意,没有 "directors" 对象。此外,嵌入列可以像平常一样被别名化。
您可以使用它来获取多对多关系中联接表的列。例如,要获取电影及其演员,但包括角色表中的 character 列
# curl "https://:3000/films?select=title,actors:roles(character,...actors(first_name,last_name))&title=like.*Lighthouse*"
curl --get "https://:3000/films" \
-d "select=title,actors:roles(character,...actors(first_name,last_name))" \
-d "title=like.*Lighthouse*"
[
{
"title": "The Lighthouse",
"actors": [
{
"character": "Thomas Wake",
"first_name": "Willem",
"last_name": "Dafoe"
}
]
}
]
注意
扩展运算符 ... 来自 Javascript 的 扩展语法。